Biometrics
Biometrics refers to the use of analytical tools and devices which capture, record and/or process people’s physical or behavioural data. This can include faces (commonly known as facial recognition), fingerprints, DNA, irises, walking style (gait), voice as well as other characteristics. Under the EU’s data protection laws, this biometric data is especially sensitive. It is linked to our individual identities, and can also reveal protected and intimate information about who we are, where we go, our health status and more. When used to indiscriminately target people in public spaces, to predict behaviours and emotions, or in situations of imbalances of power, biometric surveillance such as facial recognition has been shown to violate a wide range of fundamental rights.
Filter resources
-

Who, What, Why? Your guide to all things ECI! #ReclaimYourFace
Calling all digital rights heroes: EDRi needs your support! As part of the Reclaim Your Face campaign, we are running a European Citizens’ Initiative (ECI) to ban biometric mass surveillance practices in the EU. To be successful, we need to collect 1 million signatures. Read more to find out how we keep ECI data safe, and how your signature can make a big difference.
Read more
-

Roma & Sinti rights, Resistance & Facial Recognition: RYF in Conversation…
For communities that have been historically sidelined, the promises of digitalisation can instead become a vessel for yet more discrimination and unequal treatment. Facial recognition in particular has a sinister and dark history which links to the persecution of Romani communities. If you missed our webinar on Roma and Sinti rights and the rise of facial recognition across Europe, you can catch up here and learn what the digital rights community can and should do!
Read more
-

Romani rights and biometric mass surveillance
The rights of Romani people should be an important topic for anyone that cares about digital rights. In this blog, hear from experts in Roma, Sinti and digital rights about why facial recognition is an important issue (and what the rest of the digital rights community can learn), and check out the Reclaim Your Face campaign’s first ever resource in the Sinti language!
Read more
-

No place for emotion recognition technologies in Italian museums
An Italian museum trials emotion recognition systems, despite the practice being heavily criticised by data protection authorities, scholars and civil society. The ShareArt system collects, among others, age, gender and emotions of people. EDRi member Hermes Center called the DPA for an investigation.
Read more
-

They can hear you: 6 ways tech is listening to you
Voice recognition technology often violates human rights, and it’s popping up more and more. Recently EDRi's member Access Now called out Spotify for developing voice recognition tech that claims to be able to detect gender and emotional state, among other things. But it’s not just Spotify. Some of the most powerful companies in the world are deploying similar abusive tech because harvesting data about you is profitable. The market for voice recognition is growing, expected to be worth a whopping $26.8 billion by 2025.
Read more
-

EU privacy regulators and Parliament demand AI and biometrics red lines
In their Joint Opinion on the AI Act, the EDPS and EDPB “call for [a] ban on [the] use of AI for automated recognition of human features in publicly accessible spaces, and some other uses of AI that can lead to unfair discrimination”. Taking the strongest stance yet, the Joint Opinion explains that “intrusive forms of AI – especially those who may affect human dignity – are to be seen as prohibited” on fundamental rights grounds.
Read more
-

Biometric mass surveillance flourishes in Germany and the Netherlands
In a new research report, EDRi reveals the shocking extent of biometric mass surveillance practices in Germany, the Netherlands and Poland which are taking over our public spaces like train stations, streets, and shops. The EU and its Member States must act now to set clear legal limits to these practices which create a state of permanent monitoring, profiling and tracking of people.
Read more
-

Booklet: Depths of biometric mass surveillance in Germany, the Netherlands and Poland
In a new research report, EDRi reveals the shocking extent of unlawful biometric mass surveillance practices in Germany, the Netherlands and Poland which are taking over our public spaces like train stations, streets, and shops. The EU and its Member States must act now to set clear legal limits to these practices which create a state of permanent monitoring, profiling and tracking of people.
Read more
-
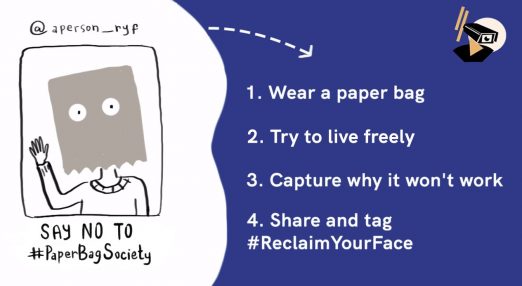
The #PaperBagSociety challenge
The #PaperBagSociety is a social media challenge part of the #ReclaimYourFace campaign that invites everyone to share online the impact of living life with a paperbag on the head. With it, we aim to raise awareness of how ridiculous is to avoid facial recognition technologies in public spaces and why we need to build an alternative future, free from biometric mass surveillance.
Read more
-

Workplace, public space: workers organising in the age of facial recognition
‘Surveillance capitalism’ is increasingly threatening workers’ collective action and the human right to public protest.
Read more
-

EDRi joins 178 organisations in global call to ban biometric surveillance
From protesters taking to the streets in Slovenia, to the subways of São Paulo; from so-called “smart cities” in India, to children entering French high schools; from EU border control experiments, to the racialised over-policing of people of colour in the US. In each of these examples, people around the world are increasingly and pervasively being subjected to toxic biometric surveillance. This is why EDRi has joined the global Ban Biometric Surveillance coalition, to build on our work in Europe as part of the powerful Reclaim Your Face campaign.
Read more
-

The urgent need to #reclaimyourface
The rise of automated video surveillance is often touted as a quick, easy, and efficient solution to complex societal problems. In reality, roll-outs of facial recognition and other biometric mass surveillance tools constitute a systematic invasion into people’s fundamental rights to privacy and data protection. Like with uses of toxic chemicals, these toxic uses of biometric surveillance technologies need to be banned across Europe.
Read more
